
The equipment-as-a-service sector is poised for monumental growth, thanks to the recent passage of three infrastructure-focused government initiatives that will inject approximately $2.1 trillion into the economy. Passed with overwhelming bipartisan support, these initiatives aim to rebuild the nation's bridges and roads and lay the groundwork for new infrastructure that is compatible with growing environmental concerns, new technology, and a move toward cleaner energy sources. This represents one of the largest infusions of federal funding into infrastructure projects to date.
As the equipment finance market prepares to capitalize on this opportunity, experts Matthew Hudson, Spencer Lippman, and Chris Sweet of Houlihan Lokey provide a comprehensive analysis of the Infrastructure Bill of 2021, Inflation Reduction Act, and Chips and Science Act, and their impact on the broader sector throughout North America. Discover the pros, cons, and unknowns of these landmark initiatives and how they will shape the future of the equipment finance industry.
A LOOK AT THE LEGISLATION
The recent passage of the Infrastructure Bill of 2021, the Inflation Reduction Act, and the Chips and Science Act present a significant opportunity to bolster American infrastructure through increased funding and modernization initiatives. These efforts are expected to enhance the quality and efficiency of transportation, energy, and communication systems throughout the country, ultimately fostering improved economic growth, job creation, and heightened competitiveness on the global stage. The far-reaching positive impact of these initiatives will be felt across multiple sectors of the economy, with equipment finance and rental services poised to experience increased demand as infrastructure rebuilding gains momentum. This dedication to development lays the foundation for sustainable growth and progress across the overall economic landscape in the U.S., particularly during a time when the market is experiencing uncertainty.
The Infrastructure Bill
The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, also known as the "Infrastructure Bill," is a groundbreaking $1.2 trillion package that will allocate approximately $550 billion in new spending and $650 billion in additional capital to revitalize existing infrastructure over the next five years. This investment effectively doubles the amount of funding previously available from the federal government and will kick-start projects that are set to commence between 2023 and 2025. Since the bill's signing, more than 10,000 projects have been announced, with more to come as the rollout gains momentum. This surge in activity is expected to drive significant M&A activity and private equity interest. Currently, around $129 billion worth of projects have been announced out of the $550 billion set aside for new spending. Companies that provide equipment or services to end markets are experiencing a significant uptick in demand, directly attributable to this infrastructure investment. More than 80% of the funds apply to the following segments:
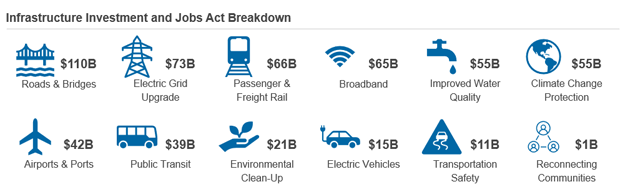
Source: Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act
The Inflation Reduction Act
The Inflation Reduction Act aims to stabilize the economy by creating strong incentives for clean energy and infrastructure development. Businesses and homeowners stand to benefit from a wave of incentives that promote energy efficiency and sustainability. These incentives, which include a range of tax credits for commercial buildings and residential homes that prioritize eco-friendliness, as well as incentives for the conversion from gas cars to electric vehicles (EV), signal a positive step toward a more sustainable future. The bill will generate approximately $390 billion, expanding infrastructure primarily funded through corporations by providing tax advantages for investments in clean energy and manufacturing over the next 10 years. However, as the demand for sustainable infrastructure development continues to surge, companies will be required to act swiftly and demonstrate flexibility to keep pace. For many, the most cost-effective approach will be to turn to rental equipment rather than committing to purchasing new equipment outright. This approach not only ensures the timely completion of these urgent projects but also helps to mitigate the impact on the bottom line. The equipment-as-a-service model will be a key element in achieving the incentives available and embracing a more sustainable future. This legislation also includes the construction of 13 electric vehicle and battery factories with an average cost of approximately $3.5 billion. This will result in substantial growth in the equipment rental industry, particularly driven by increased demand in the construction and manufacturing sectors, in which specialized equipment is needed. The following represents the breakdown of the bill by sector:
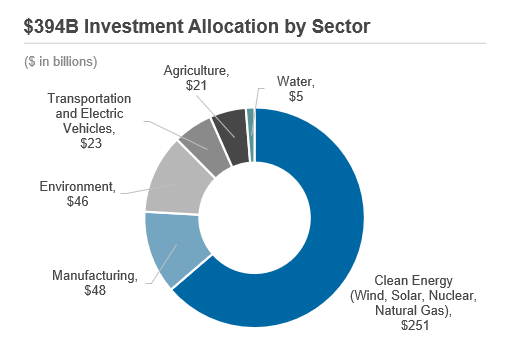
Source: Inflation Reduction Act
The Chips and Science Act
The Chips and Science Act allocates approximately $250 billion to domestic semiconductor manufacturing, which will further fortify the industry by creating incentives for companies to invest in it. This has resulted in nine new semiconductor facility projects commencing in 2022, with an average cost of approximately $7.5 billion. A small amount of funding will also go toward pollution control, artificial intelligence, and biomanufacturing projects. It is important to note that projects must start by December 2026 to qualify for funding. This will not only accelerate growth in these industries in the short term, but it will also bring more jobs back to the United States from overseas. Tech giant Micron has kick-started the "reshoring effort" by disclosing its plan to inject $40 billion into chip manufacturing, resulting in 40,000 American job opportunities and elevating the United States' market share in memory chip production from about 2% to approximately 10%. The executive order will lower product costs and ensure the manufacturing of critical technologies in the U.S., thus decreasing reliance on foreign supply chains. The resurgence of manufacturing jobs in the United States will be a significant catalyst for activity within the equipment-as-a-service industry.
State Impact
One aspect that is essential to consider is the impact of this legislation on a state-by-state basis. The Infrastructure Bill includes an element of state funding and implementation. State governments will need to develop a comprehensive plan for capital deployment, including trackable data and cost analysis, to ensure efficient spending. Some states may be better suited financially and operationally to match the deployment of funding and secure approvals to get the federal dollars needed to kick-start operations. Significant investment from each state is required to develop and publish a comprehensive timeline for implementation of funding, which could impact the speed of deployment. In addition, it is important to consider when the funding is received, state governments may need to contribute additional dollars to certain projects as timelines change, potentially exceeding the budgeted grant. This highlights the need for capital deployment planning and tracking at a more substantial level than state governments have experienced for infrastructure projects in the past.
A LOOK AT THE PROS: GROWTH, DEMAND, AND COMMITTED PUBLIC DOLLARS
The capital behind these bills is just beginning to make its presence felt in the market. Despite a period of stagnation last year, several projects are now beginning to roll out, fueled by committed dollars from the government. As a result, large equipment service providers are experiencing a significant backlog and record-high utilization metrics as they try to keep pace with rising demand. According to the Associated Builders and Contractors Organization, the average construction backlog stood at 9.2 months as of January 2023, underscoring the exploding demand for these services. The Dodge Momentum Index (DMI), which tracks non-residential market demand, recently achieved its highest-ever rating of 207.2, indicating a forthcoming expansion of construction over the next 12 months. This index has previously proven to be an early indicator of market growth, with signs of expansion noted a full year before the eventual turnaround in the construction market in 2012, following the recession of 2008.
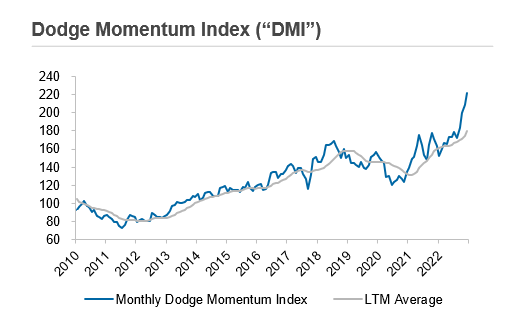
Source: Dodge Construction Network
In the construction industry, outsourcing has become a more popular option for leading companies due to rising equipment prices. The rental model has proven to be a cost-efficient alternative to purchasing equipment and eliminates the risks of asset obsolescence that come with ownership. This trend has driven demand for rental services, leading providers to expand their fleet and create value through an expansive geographic network, oftentimes engaging in M&A activity.
The emergence of projects over $400 million, known as "Mega Projects”, is a significant outcome of new legislation that has resulted in a major paradigm shift in the industry. These projects represent almost 30% of all non-residential construction, compared to 13% from 2000 to 2009. The scale and complexity of these projects require rental suppliers with financial capacity, scale, and geographic coverage to deliver, monitor, and service equipment efficiently. Therefore, equipment-as-a-service businesses will be the primary beneficiaries of this trend. Equipment-as-a-service is an emerging strategy style in which companies rent or lease equipment and offer incremental value-add services or a complete outsourced solution. This approach contrasts with the traditional rental model of simple asset delivery.
United Rentals, Ashtead Group, WillScot Mobile Mini, and McGrath RentCorp are examples of companies that fall under the equipment-as-a-service category. They have positioned themselves strategically to provide large-scale services across a broad landscape, primarily through acquisition, greenfield expansion, and the broadening of equipment and services offerings. As a result of the new legislation, valuations of these public companies in the sector, as well as the broader rental services space across North America, have increased. EBITDA multiples have remained strong in recent years, with a significant upswing in 2021 correlated with the thriving market. Valuations have remained high through 2022 and Q1 2023 with help from the previously discussed infrastructure commitments.
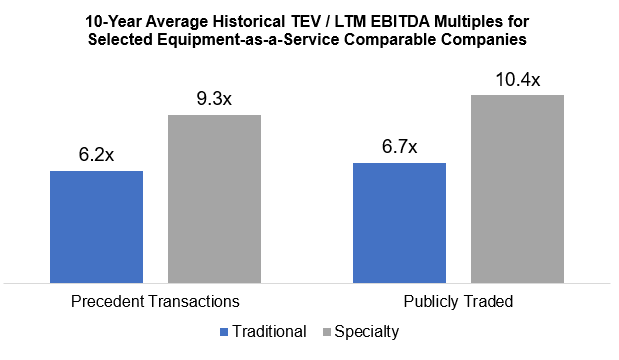
Source: Factset
Equipment service providers have a unique advantage in today's market, offering their extensive fleet to fulfill the influx of projects by providing value through greater flexibility and fewer upfront capital demands for equipment. The industry has seen record-high revenue and EBITDA figures from top industry leaders in 2022, directly attributed to the government's infrastructure investment. In anticipation of large-scale projects, companies are quickly ramping up their investments in equipment to ensure an adequate mix and availability. One notable example is United Rentals, a leader in the equipment-as-a-service industry, which increased its net rental capital expenditure by 22% in 2022 compared to the previous year. Similarly, Herc Holdings, another rental services leader, has announced an approximately 15% increase in net fleet capital expenditures in its 2023 budget to prepare for a demanding project pipeline. These investments demonstrate the industry's commitment to meeting the growing demand for equipment and services as the project landscape evolves.
Despite a potential recession on the horizon, the positive impact of these bills is that these funds are committed and public dollars should continue to flow to these projects. This will act as a cushion in the event of a recession, as the infrastructure side can support other end markets through the tough times. In an era in which many sectors are hurting due to rising interest rates, the equipment-as-a-service industry offers a unique and cost-effective option during times of economic uncertainty.
A LOOK AT THE CONS: THE LOGISTICAL IMPACT OF HIGH DEMAND, LOOMING RECESSION
The equipment sector has been experiencing significant growth, but this has come with increased costs. For example, building a growing fleet can be expensive, as orders need to be placed well in advance and financing must be secured in a rising interest rate environment. Despite strong demand, there are increased costs associated with meeting that demand.
Supply chain delays have also become commonplace, creating a greater value for providers with available fleets. Management at top providers has shifted to placing sizeable orders with vendors in anticipation of an increasing influx of projects. During a recent earnings call, the CEO of Herc Holdings informed investors that the industry is still experiencing delays of between 30 and 90 days on equipment from vendors.
Increased borrowing rates have brought various capital markets concerns on the debt side, raising questions about the appetite of lenders to support the continued growth of these businesses. There is a risk that this will outweigh the positive benefits of the Infrastructure Bill, despite the strong end-user demand. For example, if a company has a 3% interest rate debt that’s fixed but due to refinance in 2023 when rates are significantly higher, it’s not sustainable. This creates a potential balance sheet issue, not an end-market issue.
The debt markets for these companies have tightened due to concerns around inflation, higher borrowing costs, and a potential recession. Despite the strong benefits of the Infrastructure Bill, there is a dichotomy in the sector as the counterweight of rising interest rates and borrowing costs remains. The sector still resonates quite well with lenders, but a rising area of concern is a potential equity hole created by the higher cost of capital.
Demand is certainly a strong driver of growth for these companies, but the rising borrowing costs can create a greater need for either equity or flexible junior capital solutions to fill in the gap. As a result, investors are keeping a close eye on these companies and weighing the risks and rewards associated with investing in them.
Continued on Page 2...